Cloud computing has revolutionized the way we do business and interact with technology. From its humble beginnings to its current state, the cloud has transformed IT infrastructure and software delivery. In this blog post, we will explore the evolution of cloud computing, focusing on the key models of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). This comprehensive guide is tailored for tech enthusiasts and IT professionals looking to deepen their understanding of cloud computing’s past, present, and future.
Introduction to Cloud Computing
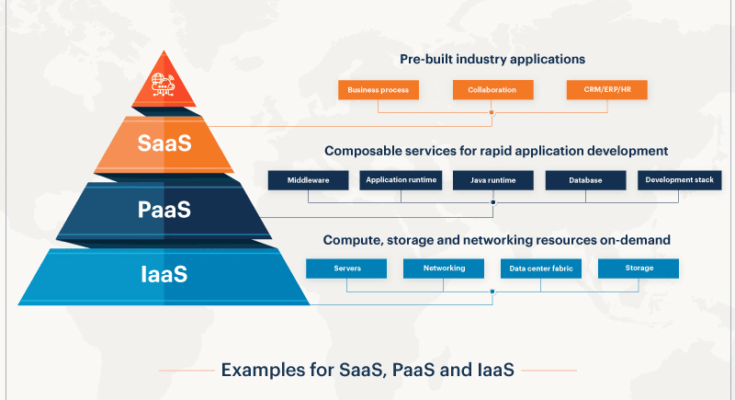
Defining IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Cloud computing is a model that allows on-demand access to a shared pool of computing resources. It typically includes storage, applications, and services that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort. Three main service models define the cloud computing landscape:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It offers essential building blocks such as virtual machines, storage, and networks.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers hardware and software tools over the internet. Developers use these tools to build and deploy applications, without worrying about underlying infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers software applications over the internet. Users access these applications via a web browser, without needing to install or maintain the software themselves.
Importance of Understanding Cloud Models
Understanding these cloud models is crucial for anyone involved in IT or technology. Each model offers distinct advantages and use cases, making it vital to grasp their differences and applications. This knowledge helps in making informed decisions about which cloud services to adopt and how to best utilize them.
What to Expect
In this blog post, we will trace the historical development of cloud computing, analyze the roles and impacts of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, and explore current trends and future predictions. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of cloud computing’s evolution and its significance in today’s tech landscape.
A Historical Overview
Early Days of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing’s roots can be traced back to the 1960s when computer scientists like John McCarthy envisioned a future where computing power would be provided as a utility. However, it wasn’t until the early 2000s that cloud computing began to take shape as we know it today.
Milestones in Cloud Development
Several key milestones marked the evolution of cloud computing:
- 2006: Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched its Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) service, offering scalable virtual servers. This marked the beginning of IaaS.
- 2008: Google introduced App Engine, a PaaS service that allowed developers to build and run applications on Google’s infrastructure.
- 2011: Microsoft launched Office 365, a SaaS offering that provided productivity tools like Word and Excel over the internet.
Early Adoptions and Challenges
Early adopters of cloud computing were often tech-savvy companies looking to reduce costs and increase flexibility. However, challenges such as security concerns, data privacy issues, and the need for reliable internet connectivity slowed widespread adoption in the beginning.
IaaS and PaaS
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It offers several benefits, including cost savings, scalability, and flexibility. With IaaS, businesses can rent virtual machines, storage, and networks on a pay-as-you-go basis, avoiding the need for significant capital investments in physical hardware.
Key Benefits of IaaS:
- Scalability: Easily scale up or down based on demand.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for what you use, reducing capital expenditures.
- Flexibility: Customize virtual environments to meet specific needs.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a platform and environment for developers to build, test, and deploy applications. It abstracts the underlying infrastructure, allowing developers to focus on coding and application logic.
Key Benefits of PaaS:
- Simplified Development: Streamlines the development process with pre-built tools and services.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Speeds up application deployment by handling infrastructure management.
- Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration among development teams through shared tools and environments.
Comparing IaaS and PaaS
While both IaaS and PaaS offer valuable services, they cater to different needs:
- IaaS: Ideal for businesses that require complete control over their infrastructure and need to build applications from scratch.
- PaaS: Suited for developers looking to streamline the development process and focus on coding rather than infrastructure management.
SaaS Emergence and Its Impact
The Rise of Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS has become the most widely recognized model of cloud computing. It delivers software applications over the internet, allowing users to access them through a web browser without the need for installation or maintenance.
Key Attributes of SaaS:
- Accessibility: Access software from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Maintenance-Free: Providers handle software updates and maintenance.
- Subscription-Based: Pay for software on a subscription basis, often with flexible pricing tiers.
SaaS in the Business World
SaaS has transformed the way businesses operate by offering a wide range of applications, from customer relationship management (CRM) systems to project management tools. It has democratized access to powerful software, enabling small and medium-sized businesses to compete with larger enterprises.
Examples of Popular SaaS Applications:
- Salesforce: A leading CRM platform that helps businesses manage customer relationships.
- Slack: A collaboration tool that facilitates communication and teamwork.
- Zoom: A video conferencing platform that has become essential for remote work.
Transformative Impact of SaaS
SaaS has revolutionized software delivery, making it easier for businesses to adopt new technologies and stay competitive. It has also driven innovation by enabling rapid deployment and iteration of software applications.
The Current Landscape
Cloud Computing in IT and Business Environments
Today, cloud computing is a fundamental component of IT and business environments. It enables organizations to scale their operations, enhance collaboration, and innovate at a faster pace.
Key Trends in Cloud Adoption:
- Hybrid Cloud: Combining public and private clouds for greater flexibility and security.
- Multi-Cloud Strategies: Using multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize performance.
- Edge Computing: Bringing computation and data storage closer to the data source for lower latency.
Cloud’s Role in Digital Transformation
Cloud computing plays a crucial role in digital transformation initiatives, helping businesses modernize their IT infrastructure, improve customer experiences, and drive efficiency.
Examples of Digital Transformation with Cloud:
- Retail: E-commerce platforms leveraging cloud services for scalability and enhanced customer experiences.
- Healthcare: Hospitals using cloud-based systems for patient records and telemedicine services.
- Finance: Banks adopting cloud solutions for secure and efficient transactions.
Security and Compliance in the Cloud
Security and compliance remain top priorities for organizations using cloud services. Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures and offer tools to help businesses meet regulatory requirements.
Key Security Practices:
- Encryption: Protecting data with encryption both in transit and at rest.
- Access Controls: Implementing robust access controls to restrict data access.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Continuously monitoring cloud environments for potential threats and conducting regular audits.
Future Trends
Predictions for Cloud Computing
The future of cloud computing is bright, with several exciting trends on the horizon:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Cloud platforms will increasingly incorporate AI and machine learning capabilities to provide advanced analytics and automation.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless architectures will enable developers to build and deploy applications without managing infrastructure.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing will revolutionize complex problem-solving and data analysis, with cloud providers exploring quantum computing services.
Innovations in Cloud Technology
Innovation in cloud technology continues to accelerate, driven by advancements in hardware, software, and networking.
Notable Innovations:
- GPU-Accelerated Computing: Leveraging GPUs for high-performance computing tasks, such as AI model training.
- Blockchain Integration: Integrating blockchain technology into cloud platforms for enhanced security and transparency.
- IoT and Cloud Convergence: Connecting IoT devices to the cloud for real-time data processing and analytics.
Preparing for the Future
To stay competitive in the evolving cloud landscape, organizations should invest in continuous learning, stay informed about emerging technologies, and be agile in adopting new solutions.
Steps to Prepare:
- Continuous Learning: Encourage employees to pursue certifications and training in cloud technologies.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with industry news, trends, and best practices through blogs, webinars, and conferences.
- Agility: Foster a culture of agility and innovation, enabling rapid adoption of new technologies.
Conclusion
The Ongoing Importance of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has come a long way from its early days, evolving into a critical enabler of modern business and technology. Its impact on IT infrastructure, software delivery, and digital transformation is undeniable, and its future holds even more promise.
Recap of Key Points
In this blog post, we’ve traced the evolution of cloud computing from IaaS to SaaS, explored the current landscape, and looked ahead to future trends. Understanding these cloud models and their applications is essential for tech enthusiasts and IT professionals aiming to stay ahead in the rapidly changing tech world.
Next Steps
Ready to take your cloud knowledge to the next level? Sign up for our free newsletter to receive the latest insights and updates on cloud computing trends. And for a deeper dive, consider joining our cloud computing course, where you’ll gain hands-on experience with the latest tools and technologies.
Let’s continue the conversation and explore the endless possibilities of cloud computing together.